Azure Digital Twins Integration
Overview
Microsoft’s Azure Digital Twins is an Azure-based cloud service that implements a digital twin model and hosting platform with persistent storage. For more information on Azure Digital Twins, please consult the Microsoft web page here. The Azure Digital Twins model offers a rich set of features for describing the contents of digital twins, including properties, components, inheritance, and more. The Azure Digital Twins Explorer GUI tool lets users view digital twin models and instances, as well as their relationships. The Azure Digital Twins service focuses on describing infrastructures with many components and their relationships. However, processing messages from data sources falls under the domain of other Azure services, such as Azure Functions and the Azure Event Grid, which can add complexity and limit real-time performance.
Integrating the ScaleOut Digital Twins™ service with Azure Digital Twins leverages ScaleOut’s in-memory computing platform to add real-time analytics with fast message processing and scalability that can handle thousands of data sources. In addition, ScaleOut Digital Twins enables continuous data aggregation and visualization of digital twin properties hosted in Azure Digital Twins. This integration unlocks a wide range of new cases that demand fast, scalable message processing to track numerous data sources, immediately detect emerging issues. and respond in the moment. These applications need to maintain maximum situational awareness while analyzing potentially huge volumes of incoming telemetry that are beyond the ability of personnel to manually track.
Nomenclature
In the following sections, the term Azure Digital Twins refers to Microsoft’s cloud service. The term Azure digital twin refers to a digital twin (model or instance) running in the service.
Note
In this document, an Azure digital twin instance refers to a deployed digital twin running in the Azure Digital Twins service, not an instance of the service. (This may differ from Microsoft documentation’s usage.)
Integration Features
The ScaleOut Azure Digital Twins Integration lets the application developer add a real-time component to an Azure digital twin model. This real-time component is implemented by a ScaleOut real-time digital twin. As defined in the introductory section, a real-time digital twin defines state information (that is, a set of properties) and a message-processing method that hosts real-time analytics.
The following sections describe how a real-time digital twin instance integrates with its corresponding Azure digital twin to:
store properties,
process messages from the data source, and
access properties in other Azure digital twin instances.
The last section describes how the ScaleOut Digital Twins service connects to the Azure Digital Twins cloud service.
In-Memory Properties
The ScaleOut Digital Twins service keeps an in-memory copy of each real-time digital twin’s properties and also stores them in an instance of an Azure Digital Twin as a component of the instance’s model. By doing this:
Azure Digital Twins can track properties used by the message-processing method for real-time analytics and make them available to Azure Digital Twins Explorer for visualization.
ScaleOut Digital Twins can immediately access the in-memory copy of these properties to accelerate message processing and to perform continuous data aggregation.
Azure Digital Twins can persist real-time digital twin properties in offline storage so that they are available after service restarts.
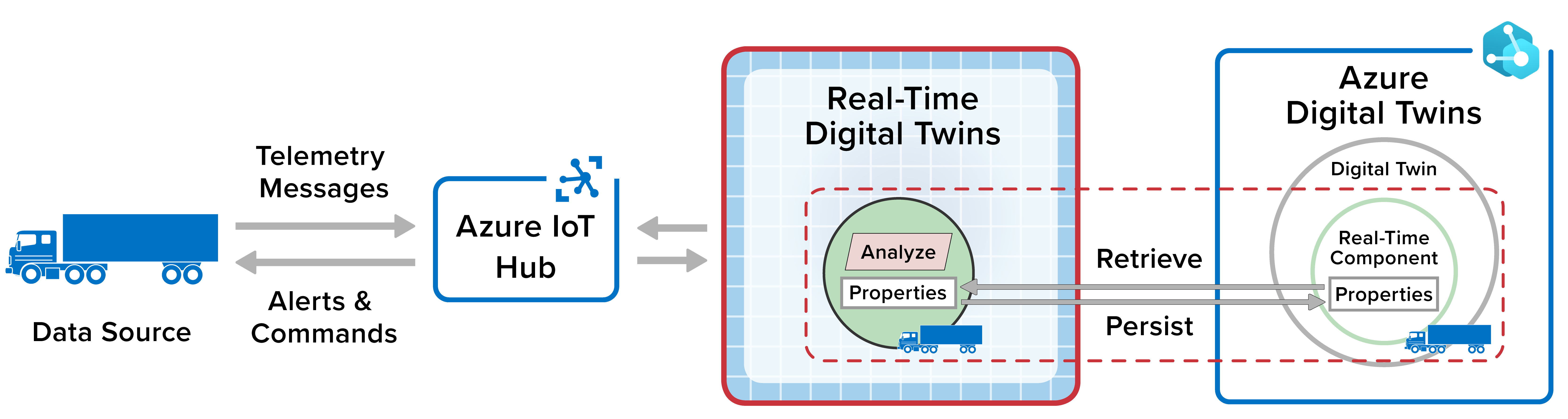
The relationship between a ScaleOut real-time digital twin and an Azure digital twin is illustrated in the following diagram. Note that the ScaleOut Digital Twins service can connect to the Azure IoT Hub, as shown in the diagram, or to other message sources to receive messages from data sources:

When it receives the first message from a data source, the ScaleOut Digital Twins service automatically attempts to load real-time properties into memory from Azure Digital Twins as part of creating a real-time digital twin instance to track the data source. If no corresponding Azure digital twin exists, the properties are initialized with default values. The service also periodically saves its in-memory copy of real-time properties as they are updated during message processing. This refreshes their values in Azure Digital Twins. If no Azure Digital Twins instance exists when its properties are updated, a new instance will automatically be created.
Here’s an example of combining a ScaleOut real-time digital twin with an Azure digital twin in a telematics application. The following diagram shows an Azure digital twin tracking telemetry from each truck in a fleet. The Azure digital twin makes use of a ScaleOut real-time digital twin to process incoming telemetry from the truck and analyze this telemetry for anomalies that need alerting. In this example, telemtry flows from the truck through Azure IoT Hub to the real-time digital twin:
ScaleOut Software provides command-line tools for developers to automatically create an Azure Digital Twins model definition for the properties defined in a real-time digital twin. This avoids the need to manually create the model definition, which just needs to be uploaded to the Azure Digital Twins service. The tool is able to generate Azure component properties for complex data structures, such as event lists and eumerated types. You can add the generated component to an existing Azure digital twin model. Alternatively, you can create a new Azure digital twin model using the generated component.
Message Processing
A ScaleOut real-time digital twin processes incoming messages from each data source using its digital twin instance’s properties. You can implement message processing code for a real-time digital twin model in C# or Java, using intuitive business rules, or by configuring machine learning algorithms.
Message-processing code runs in ScaleOut’s in-memory computing platform to accelerate performance. The platform connects to message hubs like Azure IoT Hub and automatically directs messages from each data source to its respective real-time digital twin instance. It also immediately accesses the instance’s properties from memory-based storage. These mechanisms and other optimizations minimize message-processing latency and ensure scalable processing to handle thousands of data sources.
The ScaleOut Azure Digital Twins Integration lets Azure Digital Twins take advantage of fast, in-memory performance and avoid overheads associated with the use of Azure Functions and the Azure Event Grid to implement message processing. For example, it avoids the need for serverless functions to repeatedly authenticate with Azure Digital Twins and access remote state.
APIs for Property Access
ScaleOut’s real-time digital twin model includes C# and Java APIs for reading and updating properties in Azure digital twin instances within message-processing methods. These APIs avoid the need to use multiple serverless functions to perform property updates in Azure Digital Twins.
For example, consider the Azure Digital Twins tutorial example redrawn below that shows how Azure functions can process messages from a thermostat and update both its digital twin and a parent digital twin that models the room in which the thermostat is located:

By using ScaleOut’s APIs, the message-processing method directly updates the parent object and eliminates the need for serverless functions:

The APIs let the message-processing method retrieve or update selected properties stored within Azure digital twin instances. The APIs include methods to:
retrieve the list of Azure digital twin models
retrieve the list of digital twin instances in an Azure digital twin model
retrieve the JSON model definition for an Azure digital twin model
retrieve a property from an Azure digital twin instance
save a property to an Azure digital twin instance
Details on using the APIs are described in the topic API Libraries for the ScaleOut Digital Twin Builder™ Software Toolkit.
Generating Azure Digital Twin Model Definitions
Once you have created a real-time digital twin model, you can automatically generate an Azure Digital Twins model definition in a JSON-formatted file suitable for uploading to the Azure Digital Twins service. The model definition file contains the properties defined in the real-time digital twin model and allows an Azure Digital Twins model to include a component that contains these properties. This component either can be added to an existing Azure Digital Twins model definition or can be used as a new Azure Digital Twins model.
The ScaleOut Digital Twin Builder Software Toolkit includes two model generator tools, one for Java-based real-time digital twin models, and another for C# or rules-based models (including models with machine learning algorithms). Details on using these tools can be found in the topic Azure Digital Twins Model Generator Tools.
After you upload a model definition file to the Azure Digital Twins service, you are ready to deploy the real-time digital twin model to the ScaleOut Digital Twins service, connect to the Azure Digital Twins Service (as described below), connect to a message source, such as Azure IoT Hub, and then start processing messages from your data sources.
Connecting to the Azure Digital Twins Service
To enable integration with the Azure Digital Twins service, a connection to the service must be established prior to deploying real-time digital twin models in ScaleOut Digital Twins. ScaleOut provides a connector for this purpose, as described in the topic Connectors. This connector accepts the user’s account credentials and then establishes an authenticated connection to the Azure Digital Twins service. Real-time digital twins use this connection to retrieve and persist properties, and message-processing code uses the connection to access properties in Azure digital twin instances.
Resource Limitations in Azure Digital Twins
The Azure Digital Twins service imposes numerous limits on resource usage by digital twins deployed in the service. You can find information on these resource limits here. These limits constrain the amount of property data that real-time digital twin instances can store in their corresponding Azure digital twins (currently 32KB), as well as the rate at which properties in Azure digital twins can be created (currenly 50 digital twins per second by default) and updated (currently 1000 updates per second by default).
ScaleOut Digital Twins was designed to support many thousands (or even millions) of real-time digital twins and high message-processing rates. While it performs high volume message processing on behalf of Azure digital twins, it can be configured to throttle its updates to the Azure Digital Twins service to meet these resource limits. (Details on throttling updates can be found in the topic Connectors.) In this manner, ScaleOut Digital Twins can dramatically scale the effective message-processing throughput of Azure Digital Twins.